My Daughter Stopped Studdering and Started Again
Every bit toddlers and preschoolers become increasingly exact, they may begin to stumble over their words—raising concerns about stuttering. Equally a parent, how do you know when disfluencies are a normal office of development and when to exist more concerned? Read on.
What are Typical Disfluencies?
It is not uncommon for young children to have disfluencies in their speech (eastward.1000., discussion or phrase repetitions). In fact, about 5% of all children are probable to be disfluent at some point in their development, usually between ages two ½ and 5. It is also very typical for a kid to get back and forth betwixt periods of fluency and disfluency. Sometimes, this can occur for no apparent reason, but often this happens when a child is excited, tired, or feels rushed to speak.
Learning language rules:
During this time, children are expanding their vocabularies rapidly and learning complex language rules. These rules permit children to change simple messages ("Mommy juice") into longer, more than complicated sentences that require more motor coordination to produce smoothly ("Mommy put the juice in the blue cup"). Information technology's only natural that at that place may be some disruptions forth the way.
Is Information technology Truly Stuttering?
For most toddlers and preschoolers, nearly disfluencies become away on their own after a short period of fourth dimension. In other cases, disfluencies persist and the signs of stuttering become more obvious. Getting professional assist early on offers the best chances for reducing stuttering. But how can parents tell the difference between typical disfluency that volition go away and the early signs of non-typical disfluencies that may indicate stuttering?
Here are some ways to differentiate typical disfluency from stuttering:
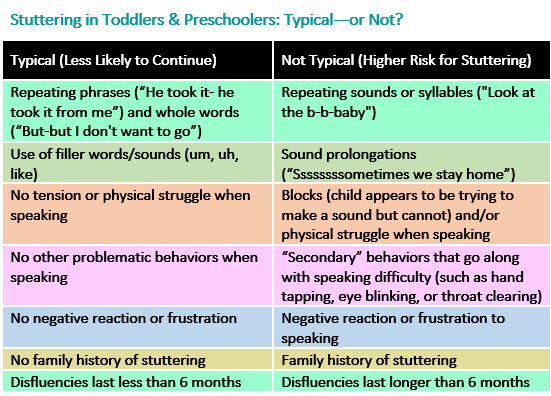
If your child is truly stuttering, he or she may agree out the offset sound in a discussion, proverb "Ssssssssometimes we stay home," or echo the sound, as in "Expect at the b-b-b-babe!" In improver, children who stutter ofttimes develop other mannerisms such as center blinking, tense mouth, looking to the side, and avoiding eye contact.
Run a risk Factors for Stuttering:
There are other run a risk factors that tin can help predict whether fluency problems will continue for longer than a few months.
-
Family history is the biggest predictor of whether a child is likely to stutter.
-
Gender. Immature boys are twice as likely as young girls to stutter, and elementary school-age boys are 3 to 4 times more likely to stutter than girls.
-
Historic period of onset. Children that commencement having difficulties at age 4 are more likely to have a persistent stutter than those who begin stuttering at a younger age.
-
Co-existing spoken language and/or language disorders increase the likelihood a child may stutter.
Getting Assist:
If you lot are concerned most your child's speech, talk with your pediatrician about getting a speech communication and language evaluation. A complete evaluation from a certified speech-language pathologist can aid you to amend decide if the stuttering is probable to persist.
Spoken language-language pathologists will assist parents determine the all-time class of action (e.chiliad., closely monitoring the child's fluency, enrolling in treatment services, and/or parent didactics). The American Speech communication-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) offers a searchable database of these professionals. In addition, a list of clinicians who specialize in stuttering can exist establish here.
Treatment Approaches for Stuttering:
Early treatment for stuttering is very of import, every bit information technology is more than probable to exist eliminated when a kid is young (before inbound simple school). In that location are two main treatment approaches for stuttering:
-
Indirect treatment is when the speech communication-linguistic communication pathologist helps the child'southward parents on how to alter their own communication styles. Indirect approaches are effective at reducing or even eliminating stuttering in many young children.
-
Directly treatment involves the speech-linguistic communication pathologist working with the children themselves either one-on-1 or in small groups, giving them specific speech strategies for easing into words and reducing tension during stuttering events. In improver, directly treatment may involve helping the child to differentiate between smooth (fluent) and bumpy (stuttered) spoken language.
After age vii, information technology becomes unlikely that stuttering will go away completely. Even so, subsequently age 7, handling tin can be very constructive at helping a child effectively manage stuttering—helping develop skills necessary to handle difficult situations (east.g., teasing and bullying) and participate fully in schoolhouse and activities. For older children, speech treatment is all the same benign, encouraged, and constructive in helping to reduce the severity and impact of stuttering.
What Parents Can Do:
Here are some means parents can assist:
-
Reduce communication stress. There are different techniques to put less pressure on a child in a speaking situation. Rephrasing questions equally comments (using "You played exterior today at school. It must have been fun!" instead of "What did you exercise at school?") is one effective approach. Parents can likewise do their best to reduce situations that trigger their kid'due south stuttering.
-
Talk virtually information technology. When children are aware of their stuttering, information technology is best to be open up and talk about information technology in a positive style. Let them know it is okay to have "bumpy speech." If a kid does not seem to be aware of the trouble, there is no need to bring it up until y'all are seeing a speech-language pathologist.
-
Do patience. Give children time to finish what they are proverb. Don't rush or interrupt them. Don't tell them to "slow downwardly" or "think about what you want to say." Phrases such every bit those are generally non helpful to children who stutter.
-
Model good speech habits. While telling a child how to talk is generally non helpful, parents can model speech habits that help with stuttering, such as slowing downwards their ain speed when they talk, putting in more pauses between sentences, and speaking in a relaxed style.
-
Seek a professional. There are many means to notice a spoken communication-language pathologist. A child's pediatrician tin provide a recommendation. Children younger than 3 can receive a costless evaluation through their local Early Intervention Program. If a child is older than 3, parents tin contact their local public school for a free evaluation. Parents too have the option to seek out a individual speech-language pathologist with a kid at whatever age. A searchable database of these professionals is available hither. A list of stuttering specialists is available here.
Follow Your Instincts:
If yous continue to accept concerns nearly your kid's oral communication, ask for a reevaluation or referral for additional formal testing.
Additional Information & Resource:
-
How to Heighten Concerns nigh a Child's Speech and Language Development
-
Learn the Signs. Act Early on (CDC.gov) - Aims to improve early identification of children with autism and other developmental disabilities so children and families can go the services and support they need.
-
Stuttering (ASHA)
-
Childhood Fluency Disorders (ASHA)
-
National Stuttering Clan
-
Stuttering Foundation
The information contained on this Web site should not exist used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. At that place may exist variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Source: https://www.healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/toddler/Pages/Stuttering-in-Toddlers-Preschoolers.aspx
0 Response to "My Daughter Stopped Studdering and Started Again"
Post a Comment